NDA WRITTEN EXAM
30+ INVICTIANS DO US PROUD BY QUALIFYING NDA(II) 2023 WRITTEN EXAM.
IMPORTANT INF0RMATION FOR NDA EXAMINATION
NDA Exam Pattern
The Competitive examination comprises:
- Written examination
- Interview for intelligence and personality test – SSB interview at one of the Services Selection Centres
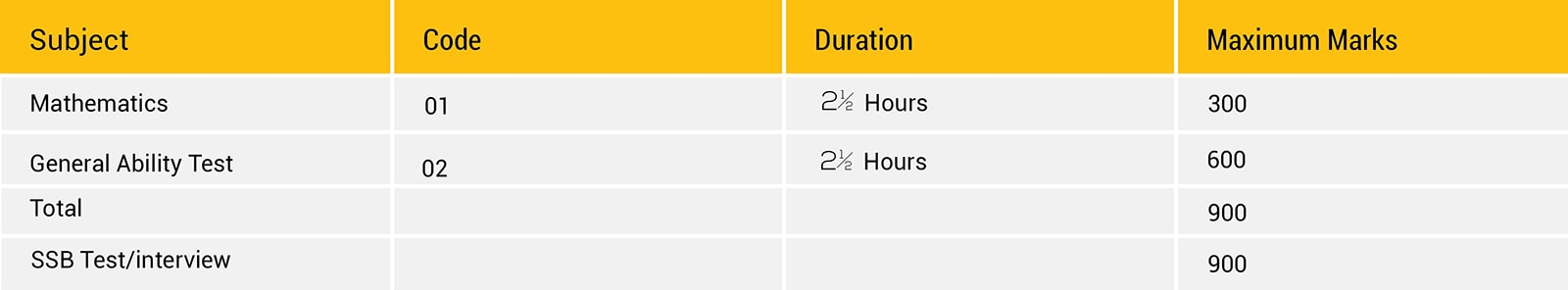
The subjects of the written examination, the time allowed and the maximum marks allotted to each subject is as follows
The papers in all the subjects will consist of Objective type questions only. The question papers (test booklets) of mathematics and part “B” of General ability test will be set bilingually in Hindi as well as English.
SYLLABUS OF THE EXAMINATION
PAPER-I MATHEMATICS (Code No. 01) (Maximum Marks-300)
1. ALGEBRA
- Concept of set, operations on sets, Venn diagrams.
- De Morgan laws, Cartesian product, relation, equivalence relation.
- Representation of real numbers on a line.
- Complex numbers—basic properties, modulus, argument, cube roots of unity.
- Binary system of numbers.
- Conversion of a number in decimal system to binary system and vice-versa.
- Arithmetic, Geometric and Harmonic progressions.
- Quadratic equations with real coefficients.
- Solution of linear inequations of two variables by graphs.
- Permutation and Combination. Binomial theorem and its applications. Logarithms and their applications.
2. MATRICES AND DETERMINANTS :
- Types of matrices, operations on matrices.
- Determinant of a matrix, basic properties of determinants.
- Adjoint and inverse of a square matrix, Applications-Solution of a system of linear equations in two or three unknowns by Cramer’s rule and by Matrix Method.
3. TRIGONOMETRY :
- Angles and their measures in degrees and in radians.
- Trigonometrical ratios. Trigonometric identities Sum and difference formulae. Multiple and Sub-multiple angles. Inverse trigonometric functions. Applications-Height and distance, properties of triangles.
4. ANALYTICAL GEOMETRY OF TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS:
- Rectangular Cartesian Coordinate system. Distance formula.
- Equation of a line in various forms. Angle between two lines.
- Distance of a point from a line.
- Equation of a circle in standard and in general form. Standard forms of parabola, ellipse and hyperbola.
- Eccentricity and axis of a conic.
- Point in a three dimensional space, distance between two points. Direction Cosines and direction ratios. Equation two points. Direction Cosines and direction ratios. Equation of a plane and a line in various forms.
- Angle between two lines and angle between two planes. Equation of a sphere.
5. DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS :
- Concept of a real valued function–domain, range and graph of a function. Composite functions, one to one, onto and inverse functions. Notion of limit, Standard limits—examples.
- Continuity of functions—examples, algebraic operations on continuous functions. Derivative of function at a point, geometrical and physical interpretation of a derivative—applications.
- Derivatives of sum, product and quotient of functions, derivative of a function with respect to another function, derivative of a composite function. Second order derivatives. Increasing and decreasing functions. Application of derivatives in problems of maxima and minima.
6. INTEGRAL CALCULUS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS :
- Integration as inverse of differentiation, integration by substitution and by parts, standard integrals involving algebraic expressions, trigonometric, exponential and hyperbolic functions.
- Evaluation of definite integrals—determination of areas of plane regions bounded by curves—applications.
- Definition of order and degree of a differential equation, formation of a differential equation by examples. General and particular solution of a differential equations, solution of first order and first degree differential equations of various types—examples.
- Application in problems of growth and decay.
7. VECTOR ALGEBRA :
- Vectors in two and three dimensions, magnitude and direction of a vector. Unit and null vectors, addition of vectors, scalar multiplication of a vector, scalar product or dot product of two vectors. Vector product or cross product of two vectors.
- Applications—work done by a force and moment of a force and in geometrical problems.
8. STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY :
- Statistics : Classification of data, Frequency distribution, cumulative frequency distribution—examples. Graphical representation – Histogram, Pie Chart, frequency polygon – examples. Measures of Central tendency—Mean, median and mode.
- Variance and standard deviation—determination and comparison. Correlation and regression.
- Probability : Random experiment, outcomes and associated sample space, events, mutually exclusive and exhaustive events, impossible and certain events. Union and Intersection of events.
- Complementary, elementary and composite events. Definition of probability—classical and statistical—examples.
- Elementary theorems on probability—simple problems. Conditional probability, Bayes’ theorem—simple problems. Random variable as function on a sample space. Binomial distribution, examples of random experiments giving rise to Binominal distribution.
APER-II GENERAL ABILITY TEST
(Code No. 02) (Maximum Marks—600)
Part ‘A’—ENGLISH (Maximum Marks—200)
- The question paper in English will be designed to test the candidate’s understanding of English and workman like use of words. The NDA Exam syllabus covers various aspects like: Grammar and usage, vocabulary, comprehension and cohesion in extended text to test the candidate’s proficiency in English.
Part ‘B’—GENERAL KNOWLEDGE (Maximum Marks—400)
- The question paper on General Knowledge will broadly cover the subjects : Physics, Chemistry, General Science, Social Studies, Geography and Current Events.
Section ‘A’ (Physics)
- Physical Properties and States of Matter, Mass, Weight, Volume, Density and Specific Gravity, Principle of Archimedes, Pressure Barometer.
- Motion of objects, Velocity and Acceleration, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Force and Momentum, Parallelogram of Forces, Stability and Equilibrium of bodies, Gravitation, elementary ideas of work, Power and Energy. Effects of Heat, Measurement of Temperature and Heat, change of State and Latent Heat, Modes of transference of Heat. Sound waves and their properties, Simple musical instruments. Rectilinear propagation of Light, Reflection and refraction. Spherical mirrors and Lenses, Human Eye.
- Natural and Artificial Magnets, Properties of a Magnet, Earth as a Magnet.
- Static and Current Electricity, conductors and Nonconductors, Ohm’s Law, Simple Electrical Circuits, Heating, Lighting and Magnetic effects of Current, Measurement of Electrical Power, Primary and Secondary Cells, Use of X-Rays.
- General Principles in the working of: Simple Pendulum, Simple Pulleys, Siphon, Levers, Balloon, Pumps, Hydrometer, Pressure Cooker, Thermos Flask, Gramophone, Telegraphs, Telephone, Periscope, Telescope, Microscope, Mariner’s Compass; Lightening Conductors, Safety Fuses.
Section ‘B’ (Chemistry)
- Physical and Chemical changes. Elements, Mixtures and Compounds, Symbols, Formulae and simple Chemical Equations, Law of Chemical Combination (excluding problems). Properties of Air and Water.
- Preparation and Properties of Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and Carbondioxide, Oxidation and Reduction. Acids, bases and salts. Carbon—different forms. Fertilizers—Natural and Artificial. Material used in the preparation of substances like Soap, Glass, Ink, Paper, Cement, Paints, Safety Matches and GunPowder. Elementary ideas about the structure of Atom, Atomic Equivalent and Molecular Weights, Valency.
Section ‘C’ (General Science)
- Difference between the living and non-living. Basis of Life—Cells, Protoplasms and Tissues. Growth and Reproduction in Plants and Animals.
- Elementary knowledge of Human Body and its important organs.
- Common Epidemics, their causes and prevention.
- Food—Source of Energy for man. Constituents of food, Balanced Diet. The Solar System—Meteors and Comets, Eclipses.
- Achievements of Eminent Scientists.
Section ‘D’ (History, Freedom Movement etc.)
- A broad survey of Indian History, with emphasis on Culture and Civilisation.
- Freedom Movement in India. Elementary study of Indian Constitution and Administration. Elementary knowledge of Five
- Year Plans of India. Panchayati Raj, Co-operatives and Community Development. Bhoodan, Sarvodaya, National Integration and Welfare State, Basic Teachings of Mahatma Gandhi.
- Forces shaping the modern world; Renaissance, Exploration and Discovery; War of American Independence. French Revolution, Industrial Revolution and Russian Revolution.
- Impact of Science and Technology on Society. Concept of one World, United Nations, Panchsheel, Democracy, Socialism and Communism. Role of India in the present world.
Section ‘E’ (Geography)
- The Earth, its shape and size. Latitudes and Longitudes, Concept of time. International Date Line. Movements of Earth and their effects. Origin of Earth. Rocks and their classification; Weathering—Mechanical and Chemical, Earthquakes and Volcanoes. Ocean Currents and Tides
- Atmosphere and its composition; Temperature and Atmospheric Pressure, Planetary Winds, Cyclones and Anti-cyclones; Humidity; Condensation and Precipitation; Types of Climate, Major Natural regions of the World. Regional Geography of India—Climate,
- Natural vegetation. Mineral and Power resources; location and distribution of agricultural and Industrial activities. Important Sea ports and main sea, land and air routes of India. Main items of Imports and Exports of India.
Section ‘F’ (Current Events)
- Knowledge of Important events that have happened in India in the recent years. Current important world events.
- Prominent personalities—both Indian and International including those connected with cultural activities and sports.
NOTE : Out of maximum marks assigned to part ‘B’ of this paper, questions on Sections ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, ‘D’, ‘E’ and ‘F’ will carry approximately 25%, 15%, 10%, 20%, 20% and 10% weightages respectively.
Student Testimonials
-
 Kaustubh Singh Chaudhary
Kaustubh Singh ChaudharyMy SSB coaching experience was absolutely outstanding! The faculty here are expertise, communication skills, and dedication to my growth were exceptional. They provided valuable insights, asked thought-provoking questions, and tailored their approach to my specific needs. Their genuine interest and support created a comfortable and trusting environment. They challenged me to step outside my comfort zone and offered practical resources to enhance my learning. I highly recommend their coaching services for anyone seeking guidance and lasting results.
Read more -
 Abhishek Gurjar
Abhishek GurjarToo much worthy to attend guidance classes here. Assessors are trying their level best to improve you and for that they will do every possible thing that they can do. But one should also need to go through their basics in order to accomplish whatever they dream for it. And trust me you will sure accomplish if you follow their guidance thoroughly. I have this personal experience.
Read more -
 Kusum Rathore
Kusum Rathore- have this personal experience. -Abhishek Gurjar
My experience in invicta has been amazing!! the environment is extremely professional . Regular mock tests , doubt sessions and worksheets helps us too. The teachers helps us to understand everything thoroughly . Best institute for all defence exams aa well as for SSB prepartion
Read more -
 Tanishq Tomar
Tanishq TomarThe mentors here are very cooperative and influensive with the IO,GTO and Psychologist being the best in this field. The academy has a good infrastructure. For an academy only 2 years old the number of recommendations in the SSB is fantastic
Read more -
 Kavita Yadav
Kavita YadavInvicta is an excellent place to prepare for all three defence services. There is personal guidance for ssb preparation. Classes are well scheduled and informed beforehand. You are guided for all the stages of ssb interview and your weaknesses are pointed to you with sufficient suggestions to improve them. There are three teachers who are officers and have served in the forces and thus have expertise over their specific subjects. Overall I totally recommend joining the academy if you're a beginner
Read more -
 Adhiraj Shekhawat
Adhiraj ShekhawatI am so proud to be an alumnus of Invicta Defence Academy. This is one stop place for the preparation to become an officer Indian defence forces. The forte of this academy is in SSB as they have life experience in the same
Read more -
 Hardik Bajaj
Hardik BajajMy experience has been amazingg!!!! The environment is very professional, everyone is very helpful. The teachers help you to understand each and everything thoroughly. Regular mock tests, doubt sessions and worksheets helps us in understanding different kinds of questions. I believe it the best academy for defence
Read more -
 Aneesh Saini
Aneesh SainiBest environment and team work Good people and good infrastructure and good location and great experience .. Teacher are very special
Read more -
 Bharat Danu
Bharat DanuMost effective institute for the SSB.Teaching Methods are unique.Good environment to focus on our strengths and overcoming our weakness .Recommendation is another thing but you'll come out from the institute as a better version of your previous self
Read more -
 Shaurya Singh Kotecha
Shaurya Singh KotechaMy experience at Invicta has been extremely good. I have learnt a lot about the SSB and how to perform well in it. The academy has experienced faculty.Mock tests and practice sessions are held similar to the actual SSB to prepare the candidates well. Personalised attention is given to every student and counselling takes place on weekends.A great place to know your real self and to prepare for SSB.
Read more -
 Pankaj Dabas
Pankaj DabasInvicta truly is inspiring. The assessors are so dedicated and hardworking towards its students. I can see the changes in myself and have learnt a lot not just about SSB but about life as well.If you really wish to be an officer in Armed Forces, then this is the right stop for you. Be prepared to work hard and give your best. This is not just any SSB coaching, this is the institute which will show you the mirror and work on improving you.
Read more -
 Kusum Rathore
Kusum RathoreMy experience in invicta has been amazing!! the environment is extremely professional . Regular mock tests , doubt sessions and worksheets helps us too. The teachers helps us to understand everything thoroughly .Best institute for all defence exams aa well as for SSB. prepartion
Read more -
 Tanishq Tomar
Tanishq TomarThe mentors here are very cooperative and influensive with the IO,GTO and Psychologist being the best in this field. The academy has a good infrastructure. For an academy only 2 years old the number of recommendations in the SSB is fantastic
Read more -
 Yukta Bhardwaj
Yukta BhardwajBest environment and teachers are very supportive, they analys the weakness of students and work on them and also enhance the strength of an individual. I'm glad that I choose this academy for my SSB guidance
Read more -
 Kuldeep Singh Rathore
Kuldeep Singh RathoreThere is a lot of good experience here, mainly by doing SSB guidance, we have motivated a lot by our assessors.Personality development has helped a lot and the confidence level has been boosted
Read more -
 Subhash Choudhary
Subhash ChoudharyInvicta SSB coaching is a game-changer for aspiring armed forces candidates. It offers a comprehensive approach to excel in the rigorous selection process. With experienced faculty and personalized attention, it enhances knowledge, skills, and mindset. Mock tests and practice sessions simulate the actual SSB environment, fostering readiness and confidence. Peer learning cultivates healthy competition and camaraderie. SSB coaching significantly boosts chances of success, unlocking the path to a fulfilling career in the defense sector
Read more -
 shivangi pandia
shivangi pandiaInvicta is the best academy to stat your SSB preparation. Having the best GTO ground and three expert assessors who not only ace your preparation but also give genuine and one to one guidance to every student. They enhance your personality and Invicta gives you an edge over others. GTO Ground gives you a practical insight into the real SSB centre. Highly recommneded
Read more -
 Karanveer Gahlot
Karanveer GahlotThe faculty here is nice, working really hard to improve students communication, listening skills.All the process is done day by day.Real time example are also available for GTO TASK..Faculty are friendly and also have experience of Indian Army
Read more -
 Aditi Agarwal
Aditi AgarwalAt invicta academy officers do not coach their students but guide for bringing out their best version out of them. Academy's environment is disciplined itself to make one understand about their responsibilities and punctuality to be followed.If you visit the academy you will find number of students from various cities. Officers here are experienced of assessing students so one can experience exact same procedure of ssb
Read more -
 Narendra Singh
Narendra SinghInstructor of Academy is really good and knowledgeable. If there is a will power and determination in someone then he will definitely crack the ssb and this academy surely & definitely develops your personality
Read more -
 Neeraj Godara
Neeraj GodaraJoined it recently everything is pretty well. Classes are conducted as per ssb schedule which gives a thorough understanding of complete process. Evaluation is quite frank and helps in improving your performance
Read more -
 Kankshi yadav
Kankshi yadavThe academy shapes you into a trained soldier, inculcate all the OLQ qualities. Improves mental toughness and physical bearing.The faculty is run by 3 ex Army col and SSB assessors who are experts in their respective fields
Read more -
 Pardeep
PardeepFrankly speaking so i was really weak in public speaking and had some issues for pysic part but individual consuling and continuous practice of luctureete helped me to overcome that. Best place to improve one's personality and achieve dreams for which you are preparing for. Proper guidance and one to one interaction is the thing i liked the most.
Read more -
 Shauviq Mishra
Shauviq MishraInvicta has improved my overall personality. The course has helped me become more confident.The assessors here are very experienced and they will help you every step of the way.
Read more -
 Raghav Agarwal
Raghav AgarwalBest institute for all defence written exams like NDA CDS AFCAT . Full coverage of syllabus and daily practice papers for maths and twice a week for other subjects are provided and Mock tests based on PYQ's are taken on sunday. One of the best place for ssb preparation.-
Read more -
 Vaidehi Hada
Vaidehi HadaThe academy is well-equipped for GTO practices as well, and all the accessors seem genuinely engaged and concerned with the outcome of the candidate's progress. Classes are organized thoughtfully, with content presented in a logical manner and the counselling sessions are a great help too
Read more -
 Dushyant
DushyantIt is the best academy to choose if you are passionate and motivated about joining defence services. All the mentors have a great experience and are so influencing and willing to guide you so deliberately that adds to the reason of 74+ selections only in the period of two years. I will like to add, only in three weeks my personality has been enhanced with the overall guidance and influence of the mentors here added with my persistent efforts to learn more and more from them
Read more -
 Adhiraj Shekhawat
Adhiraj ShekhawatI am so proud to be an alumnus of Invicta Defence Academy. This is one stop place for the preparation to become an officer Indian defence forces. The forte of this academy is in SSB as they have life experience in the same
Read more -
 Mona Sharma
Mona SharmaIt is the best academy for not only ssb preparation but also for personality development. All mentors are well experienced and helpful, pay attention on every candidate. If you are looking for ssb guidance then must visit this academy
Read more -
 Anushka
AnushkaInvicta defense academy is an excellent academy for defence preparation as it doesn't coach but it guides an individual to become a better person in life. My experience here has been wonderful and all the mentors here are very humble and helpful in making you perfect for armed forces
Read more -
 Aaryan Singh Shekhawat
Aaryan Singh ShekhawatInvicta SSB coaching is a game-changer for aspiring armed forces candidates. It offers a comprehensive approach to excel in the rigorous selection process. With experienced faculty and personalized attention, it enhances knowledge, skills, and mindset. Mock tests and practice sessions simulate the actual SSB environment, fostering readiness and confidence. Peer learning cultivates healthy competition and camaraderie. SSB coaching significantly boosts chances of success, unlocking the path to a fulfilling career in the defense sector.
Read more -
 Rupali Yadav
Rupali YadavMy experience is amazing at Invicta defence academy. The mentors are experienced and guide you very well for the exam. Here the environment is very nice and i have learnt alot and according to me it is best to get guidance for SSB
Read more -
 Karan Singh
Karan SinghBest academy for guidance in ssb. Mentors are very experienced and provide one to one guidance. System of management is proper. And each candidate help each other for improvement and gives an excellent environment for progress
Read more -
 Kavita Yadav
Kavita YadavInvicta is an excellent place to prepare for all three defence services. There is personal guidance for ssb preparation. Classes are well scheduled and informed beforehand. You are guided for all the stages of ssb interview and your weaknesses are pointed to you with sufficient suggestions to improve them. There are three teachers who are officers and have served in the forces and thus have expertise over their specific subjects. Overall I totally recommend Joining the academy if you're a beginner
Read more -
 Rahul Shekhawat
Rahul ShekhawatToo much worthy to attend guidance classes here. Assessors are trying their level best to improve you and for that they will do every possible thing that they can do. But one should also need to go through their basics in order to accomplish whatever they dream for it. And trust me you will sure accomplish if you follow their guidance thoroughly. I have this personal experience
Read more -
 Vishal Jyani
Vishal JyaniIt is the best academy to choose if you are passionate and motivated about joining defence services. All the mentors have a great experience and are so influencing and willing to guide you so deliberately that adds to the reason of 74+ selections only in the period of two years.-
Read more -
 ARNAB BAHADUR
ARNAB BAHADURThe experience in Invicta Defense Academy has been absolutely phenomenal. The results are evident and the assessors have provided me with the most valuable and rewarding guidance. I would most definitely recommend this academy to each individual pursuing a career in defense forces
Read more -
 Miraj Azmin Barbhuiya
Miraj Azmin BarbhuiyaIt is a life changing experience here in Invicta. The methods in which the assessors are training everyone is very unique and special. I feel very happy to be here for my SSB preparation. The lessons have definitely given me a lot.-
Read more -
 Mr sharma ji
Mr sharma jiMy SSB academy experience was absolutely outstanding! The mentors here are expertise, communication skills, and dedication to my growth were exceptional. They provided valuable insights, asked thought-provoking questions
Read more -
 Bharti
BhartiThe academy is fully supportive and it not only helps the candidates to develop their personality for SSB but also for their whole life. All mentors are hardworking and dedicated to their work. If someone truly want to build their personality then he/she should must visit to this academy
Read more -
 GARVIT YADAV
GARVIT YADAVInvicta Defence Excellence Academy in Jaipur, played a pivotal role in steering me towards my goal of securing a recommendation for the armed forces. This distinguished institution is home to a triumvirate of retired officers, each with a rich background in serving across various SSBs in India. Specializing in interviewing, GTO, and psychology, they extend personalized mentorship to every aspirant, imparting lifelong skills that significantly elevate one's personality. My relentless efforts, complemented by the insightful guidance of the assessor- cum-mentors, proved instrumental in earning the coveted recommendation. Undoubtedly, this academy stands out as the premier and indispensable choice for anyone aspiring to excel in the pursuit of joining the armed forces.
Read more -
 Netal singh
Netal singhOne of the best institutes for SSB GUIDANCE in Jaipur. Here at Invicta, Mentors help in transforming personality which is the most important key to clear SSB. I myself had applied in Invicta for SSB Guidance. The personal guidance and the counseling by the mentors who themselves have served in Service Selection Board at various centers, helped me to clear SSB
Read more -
 Kaustubh Singh Chaudhary
Kaustubh Singh ChaudharyMy SSB coaching experience was absolutely outstanding! The faculty here are expertise, communication skills, and dedication to my growth were exceptional. They provided valuable insights, asked thought-provoking questions, and tailored their approach to my specific needs. Their genuine interest and support created a comfortable and trusting environment. They challenged me to step outside my comfort zone and offered practical resources to enhance my learning. I highly recommend their coaching services for anyone seeking guidance and lasting results
Read more -
 Abhishek Gurjar
Abhishek GurjarToo much worthy to attend guidance classes here. Assessors are trying their level best to improve you and for that they will do every possible thing that they can do. But one should also need to go through their basics in order to accomplish whatever they dream for it. And trust me you will sure accomplish if you follow their guidance thoroughly. I have this personal experience
Read more -
 Kusum Rathore
Kusum RathoreMy experience in invicta has been amazing!! the environment is extremely professional. Regular mock tests, doubt sessions and worksheets helps us too. The teachers helps us to understand everything thoroughly. Best institute for all defence exams aa well as for SSB prepartion
Read more -
 Tanishq Tomar
Tanishq TomarThe mentors here are very cooperative and influensive with the IO, GTO and Psychologist being the best in this field. The academy has a good infrastructure. For an academy only 2 years old the number of recommendations in the SSB is fantastic
Read more -
 Kavita Yadav
Kavita YadavInvicta is an excellent place to prepare for all three defence services. There is personal guidance for ssb preparation. Classes are well scheduled and informed beforehand. You are guided for all the stages of ssb interview and your weaknesses are pointed to you with sufficient suggestions to improve them. There are three teachers who are officers and have served in the forces and thus have expertise over their specific subjects. Overall I totally recommend Joining the academy if you're a beginner
Read more -
 Adhiraj Shekhawat
Adhiraj ShekhawatI am so proud to be an alumnus of Invicta Defence Academy. This is one stop place for the preparation to become an officer Indian defence forces. The forte of this academy is in SSB as they have life experience in the same
Read more -
 Hardik Bajaj
Hardik BajajMy experience has been amazingg!!!! The environment is very professional, everyone is very helpful. The teachers help you to understand each and everything thoroughly. Regular mock tests, doubt sessions and worksheets helps us in understanding different kinds of questions. I believe it the best academy for defence.-
Read more -
 Aneesh Saini
Aneesh SainiBest environment and team work Good people and good infrastructure and good location and great experience.. Teacher are very special
Read more -
 Bharat Danu
Bharat DanuMost effective institute for the SSB. Teaching Methods are unique. Good environment to focus on our strengths and overcoming our weakness. Recommendation is another thing but you'll come out from the institute as a better version of your previous self
Read more -
 Shaurya Singh Kotecha
Shaurya Singh KotechaMy experience at Invicta has been extremely good. I have learnt a lot about the SSB and how to perform well in it. The academy has experienced faculty. Mock tests and practice sessions are held similar to the actual SSB to prepare the candidates well. Personalised attention is given to every student and counselling takes place on weekends. A great place to know your real self and to prepare for SSB
Read more -
 Pankaj Dabas
Pankaj DabasInvicta truly is inspiring. The assessors are so dedicated and hardworking towards its students. I can see the changes in myself and have learnt a lot not just about SSB but about life as well. If you really wish to be an officer in Armed Forces, then this is the right stop for you. Be prepared to work hard and give your best. This is not just any SSB coaching, this is the institute which will show you the mirror and work on improving you
Read more -
 Kusum Rathore
Kusum Rathoremy experience in invicta has been amazing!! the environment is extremely professional. Regular mock tests, doubt sessions and worksheets helps us too. The teachers helps us to understand everything thoroughly. Best institute for all defence exams aa well as for SSB prepartion
Read more -
 Tanishq Tomar
Tanishq TomarThe mentors here are very cooperative and influensive with the IO, GTO and Psychologist being the best in this field. The academy has a good infrastructure. For an academy only 2 years old the number of recommendations in the SSB is fantastic
Read more -
 Karanveer Gahlot
Karanveer GahlotThe faculty here is nice, working really hard to improve students communication, listening skills. All the process is done day by day. Real time example are also available for GTO TASK.. Faculty are friendly and also have experience of Indian Army
Read more -
 Aditi Agarwal
Aditi AgarwalAt invicta academy officers do not coach their students but guide for bringing out their best version out of them. Academy's environment is disciplined itself to make one understand about their responsibilities and punctuality to be followed. If you visit the academy you will find number of students from various cities. Officers here are experienced of assessing students so one can experience exact same procedure of ssb
Read more
NDA WRITTEN Exam FAQ's
Invicta Defence Academy is one of the top NDA coaching centre in India. With its faculty, study materials and proven track record it stands out as top choice for NDA aspirants.
NDA exam has Maths and GAT questions covering a wide range of subjects from algebra to current events. For comprehensive preparation and personalized guidance as per the exam requirements, join Invicta Defence Academy where success is fostered through experienced coaching and focused practice.
Yes, you can crack NDA without coaching by self study, hard work and right resources. But joining a reputed coaching centre like Invicta Defence Academy will give you an edge. With expert guidance, study plans and personalized attention
NDA coaching fee in India ranges from ₹30,000 to ₹60,000. At Invicta Defence Academy we offer quality coaching at affordable prices to ensure your success!
Coaching for NDA exam is helpful because it provides structured learning, expert guidance, motivation, access to study materials and regular mock tests all of which can enhance preparation and chances of success.
Invicta Defence Academy is considered best coaching for nda because of its focused NDA classes, personal mentoring and frequent mock tests which prepares students thoroughly for NDA written exam and SSB interview.
At Invicta Defence Academy we conduct mock tests regularly, usually weekly to ensure students are well prepared and confident for NDA exam.
Joining an Online NDA coaching centre provides structured learning, expert guidance, regular practice and focused preparation for both written exam and SSB interview, chances of success will increase.
Invicta Defence Academy is best for NDA coaching in Jaipur, top NDA classes and complete support throughout the exam preparation.
The best time to join NDA coaching is right after completing Class 10th or 11th to get a strong foundation. Early start with Invicta Defence Academy. Get expert guidance and a jumpstart!
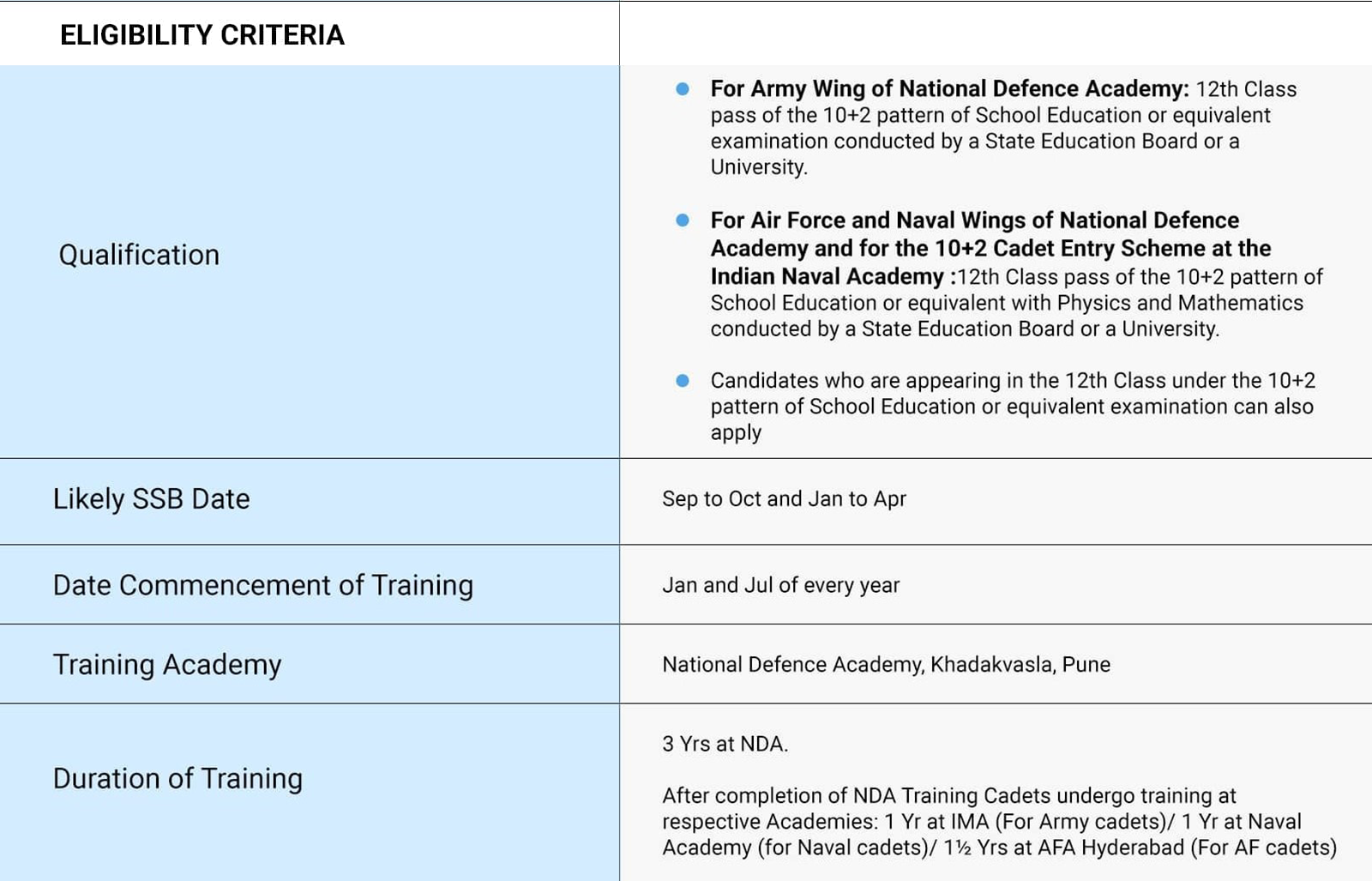
For the Army Wing of NDA, 12th passed and for Air Force and Naval Wings of NDA, 12th with Physics, Chemistry and Maths.
NDA passed Lieutenant salary is between INR 56,100-1,77,500 per month.
NDA stands for National Defence Academy. The NDA exam is conducted twice a year by UPSC.
Candidates must be 16.5 to 19.5 years old. Must have 12th class certificate.
General is the highest rank in the Indian army. Admiral in the Indian Navy and Air Chief Marshal in the Indian Air Force.
Lieutenant is the first post in Indian defence forces.
NDA Online coaching is 4-6 months. At Invicta Defence Academy we have focused and result oriented programs!
Invicta Defence Academy is best NDA coaching in Jaipur, Rajasthan. With proven track record, expert faculty and infrastructure Invicta Defence Academy is the first choice of defence aspirants.



